Dive into the world of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) and discover how these technologies enhance vehicle safety and performance across various automation levels.
What is ADAS?
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) mark a progress in automotive innovation aimed, at boosting driver safety and enhancing the driving experience. These systems utilize a blend of sensors, cameras and artificial intelligence to aid drivers in tasks from basic operations to intricate navigation and obstacle avoidance. By incorporating these technologies into vehicles manufacturers strive to minimize accidents resulting from human mistakes and set the stage for fully self driving vehicles.
How Does the ADAS System Work?
The functioning of an Advanced Driver Assistance System relies, on a combination of sensors and processors. These systems collect information about the vehicles surroundings using radar, cameras and lidar to form an accurate picture of the environment. This data is analyzed allowing the vehicle to make smart choices and take actions to support the driver or even drive autonomously in situations.
The integration of data from sources is essential in this process. By combining information the system can effectively detect obstacles, lane markings and other important details. This ability allows vehicles to react faster than drivers improving safety and efficiency on the road.
Active and Passive Safety Systems
Active safety features – which are those that help to prevent or mitigate road crashes from occuring, or reduce the severity of an unavoidable crash.
Passive safety features – which are designed to protect vehicle occupants once a crash has occurred. (Airbags, Seat-belts)
Understanding SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) Levels
The Society of Automotive Engineers classifies Advanced Driver Assistance Systems into six levels. Level 0 indicates that the driver is in control while Level 5 signifies that the vehicle can operate independently. Each level showcases a varying level of automation and support, facilitating a gradual shift, towards self driving cars.
| Level 0: No automation. The driver is fully responsible for all vehicle operations. |
| Level 1: Driver assistance provided through features like adaptive cruise control. |
| Level 2: Partial automation. The vehicle can handle steering and acceleration but requires driver supervision. |
| Level 3: Conditional automation. The vehicle can manage most driving tasks but may require driver intervention in specific scenarios. |
| Level 4: High automation. The vehicle can operate independently within predefined conditions and geofenced areas. |
| Level 5: Full automation. The vehicle performs all driving tasks under all conditions without human intervention. |
Automotive ADAS Sensors
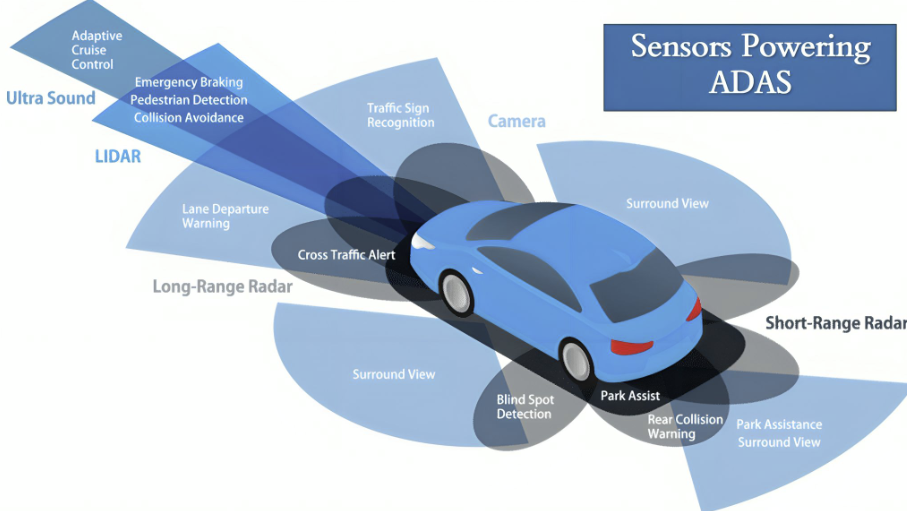
Camera Sensor
- Cameras capture high-resolution images that are processed to understand road conditions, detect road signs and identify obstacles.
- Types of Cameras
– Front-View Camera: Mounted behind the windshield, detects lanes, vehicles, pedestrians and traffic signs.
– Rear-View Camera: Assists in reversing, parking and object detection with wide-angle views.
– Surround View / 360° Cameras: Provides a bird’s eye view, combining feeds from multiple cameras.
– Side-View Camera: Monitors blind spots and lane change scenarios, enhancing driver awareness.
– Interior Cabin Camera: Monitors driver attention, fatigue levels, and passenger safety (Driver Monitoring System) - Why Cameras in ADAS?
– High-resolution object recognition.
– Accurate lane tracking and road edge detection.
– Reliable performance in urban and highway scenarios.
– Fusion-friendly with other sensors.
LiDAR Sensor
- How Does LiDAR Works?
LiDAR emits laser pulses and waits for them to reflect off objects.
It then calculates the time-of-flight to determine how far away each object is.
This data creats a 3D map of the environment around the vehicle. - Types of LiDAR
– Mechanical LiDAR: Rotating parts, 360° view, Bulky.
– Solid State LiDAR: Compact, no moving parts, perfect for cars.
– Flash LiDAR: Wise-area flash, fast data, ideal for close-range. - Why LiDAR in ADAS?
– Obstacle Detection wth centimeter-level accuracy.
– Lane and Road Mapping even in poor lighting.
– Pedestrian and Object Tracking with real-time 3D perception.
– High-definition Mapping for precise navigation.
Radar Sensor
- RADAR (RAdio Detection and Ranging) is one necessary sensor for ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance System) systems for the detection and location of objects in the presence of interference; i.e., noise, clutter, and jamming.
- Transmit a radio signal toward a target, Receive the reflected signal energy from target.
- Types of Radar in ADAS
– Short Range Radar (SRR) – 0.2 to 50 meters
– Mid Range Radar (MRR) – 50 to 100 meters
– Long Range Radar (LRR) – 100 to 250+ meters - Limitations of Radar Sensors
– Lower resolution than cameras or LiDAR
– Struggles with small or non-mettalic objects
– Can create false positives in dense traffic
– Needs calibration for high accuracy
Ultrasonic Sensor
- What is a Ultrasonic Sensor?
They emit high-frequency sound waves and measure the time it takes for the echo to return. - Use Cases
– Ideal for Short-Range (0.2m to 5m).
– Works Day and Night.
– Low Cost and High Reliability. - Why Ultrasonic Sensor in ADAS?
– Compact and Affordable.
– Effective in Poor Lighting.
– Works in Tight Spaces.
IMU/GNSS System
- Global Navigation Satellite Systems and Inertial Measurement Units
- Determining Positioning, velocity, time, angular rotation rate.
ADAS Sensor Fusion
How Does Sensor Fusion Work?
Data Association: Matches data points from different sensors to the same real-world object.
State Estimation: Predicts the system’s state (e.g., Position, Speed) using algorithms like Kalman Filters.
Data Fusion: Merges data into a unified dataset for better decision-making.
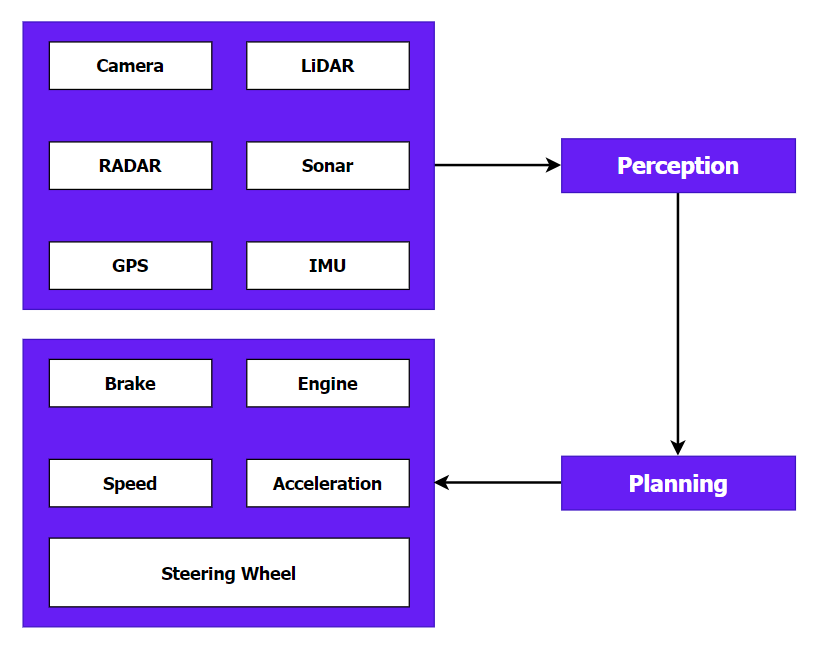
Why Sensor Fusion?
Enhanced Accuracy: Reduces noise and errors by cross-validating data from different sensors.
Robustness: Ensures system reliability even if one sensor fails.
Extended Coverage: Provides a comprehensive view of the environment by integrating diverse data types

V2X System
- Vehicle to Vehicle
- Vehicle to Motorcycle
- Vehicle to Pedestrian
- Vehicle to Infrastructure
- Vehicle to object/device
Key ADAS Features
𝟭. 𝗔𝗱𝗮𝗽𝘁𝗶𝘃𝗲 𝗖𝗿𝘂𝗶𝘀𝗲 𝗖𝗼𝗻𝘁𝗿𝗼𝗹 (𝗔𝗖𝗖): Maintains a safe distance from the car ahead by adjusting speed.
𝟮. 𝗟𝗮𝗻𝗲 𝗗𝗲𝗽𝗮𝗿𝘁𝘂𝗿𝗲 𝗪𝗮𝗿𝗻𝗶𝗻𝗴 (𝗟𝗗𝗪) & 𝗟𝗮𝗻𝗲 𝗞𝗲𝗲𝗽𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝗔𝘀𝘀𝗶𝘀𝘁 (𝗟𝗞𝗔): Warns the driver if drifting from the lane and corrects steering.
𝟯. 𝗔𝘂𝘁𝗼𝗺𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗰 𝗘𝗺𝗲𝗿𝗴𝗲𝗻𝗰𝘆 𝗕𝗿𝗮𝗸𝗶𝗻𝗴 (𝗔𝗘𝗕): Applies brakes automatically to avoid or mitigate collisions.
𝟰. 𝗕𝗹𝗶𝗻𝗱 𝗦𝗽𝗼𝘁 𝗗𝗲𝘁𝗲𝗰𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 (𝗕𝗦𝗗): Alerts the driver to vehicles in blind spots during lane changes.
𝟱. 𝗙𝗼𝗿𝘄𝗮𝗿𝗱 𝗖𝗼𝗹𝗹𝗶𝘀𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗪𝗮𝗿𝗻𝗶𝗻𝗴 (𝗙𝗖𝗪): Warns of impending collisions with objects ahead.
𝟲. 𝗧𝗿𝗮𝗳𝗳𝗶𝗰 𝗦𝗶𝗴𝗻 𝗥𝗲𝗰𝗼𝗴𝗻𝗶𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 (𝗧𝗦𝗥): Detects and displays road signs like speed limits.
𝟳. 𝗣𝗮𝗿𝗸𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝗔𝘀𝘀𝗶𝘀𝘁 & 𝗥𝗲𝗮𝗿𝘃𝗶𝗲𝘄 𝗖𝗮𝗺𝗲𝗿𝗮𝘀: Assists in parking and avoiding obstacles.
𝟴. 𝗗𝗿𝗶𝘃𝗲𝗿 𝗠𝗼𝗻𝗶𝘁𝗼𝗿𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝗦𝘆𝘀𝘁𝗲𝗺 (𝗗𝗠𝗦): Monitors driver attention and alerts for signs of fatigue or distraction.
𝟵. 𝗦𝘂𝗿𝗿𝗼𝘂𝗻𝗱-𝗩𝗶𝗲𝘄 𝗖𝗮𝗺𝗲𝗿𝗮𝘀: Provides a 360-degree view of the vehicle’s surroundings.
𝟭𝟬. 𝗡𝗶𝗴𝗵𝘁 𝗩𝗶𝘀𝗶𝗼𝗻: Enhances visibility in low-light conditions to detect obstacles.